The Skin Depth Converter allows you to calculate the depth to which an alternating current penetrates a conductor. The value obtained, called skin depth or δ, depends on the frequency of the signal, the resistivity and the relative permeability of the material. This conversion is essential for electronics and radio frequency engineers to properly size conductors and avoid excessive losses.
Formula
δ = √(ρ / (π × f × μ₀ × μr))
Explanation of the formula
The skin depth δ is calculated from the resistivity ρ of the material (in Ω m), the current frequency f (Hz), the vacuum permeability μ₀ and the relative permeability μr. The square root makes it possible to relate the resistivity and the inductive effect of the material on the penetration depth of the alternating current.
As the frequency increases or the permeability of the material increases, the penetration depth decreases. Likewise, a larger resistivity slightly increases the skin depth.
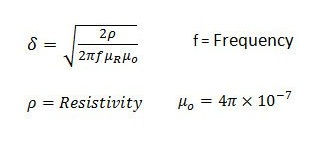
Uses
- Properly size conductors for RF and microwave circuits.
- Evaluate area losses in high frequency cables and antennas.
- Choose the appropriate material to minimize resistance and heat dissipation.
- Analyze the phenomena of AC penetration in power and signal systems.